Rail chain signal: Difference between revisions
m (→Usage examples) |
m (→Usage examples) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
With a regular signal, the block after it is empty, so the train can go there. | With a regular signal, the block after it is empty, so the train can go there. | ||
[[File:Regular-signals.png|1000px]] | [[File:Regular-signals.png|1000px]] | ||
Revision as of 14:24, 30 March 2020
| Rail chain signal |
|
Recipe |
|
| + + → | |
|
Total raw |
|
| + + |
|
Recipe |
|
| + + → | |
|
Total raw |
|
| + + |
|
Map color |
|
|
Health |
100 |
|
Stack size |
50 |
|
Mining time |
0.1 |
|
Prototype type |
|
|
Internal name |
rail-chain-signal |
|
Required technologies |
|
|
Produced by |
|
Rail chain signals are used for automated transportation on a railway network. With rail chain signals, it is possible to use multiple trains on a single track, or multiple rails that intertwine.
Basic
- The best prerequisite to understand chain signals is to understand signal blocks.
- Rail chain signals are placed like block signals at the right side of a segment.
- They work similar to pre-signals in OpenTTD.
Definition
While normal signal prevents train from entering the occupied block, chain signal prevents train from entering the block also when the exit isn't free. When more exits exist, the one relevant to the train path is taken into account.
Usage examples
Regular signal compared to a chain signal
With a regular signal, the block after it is empty, so the train can go there.

Chain signal with one exit doesn't allow the train to enter the block, since it can't leave immediately.
Simple example with practical usage
The chain signal prevents the train from blocking the crossing route while waiting.
Double crossing
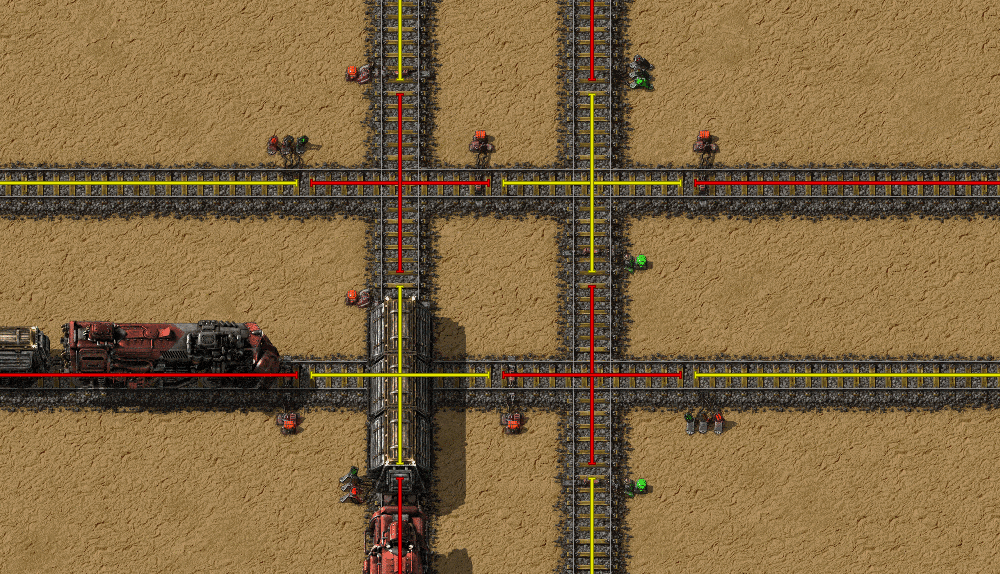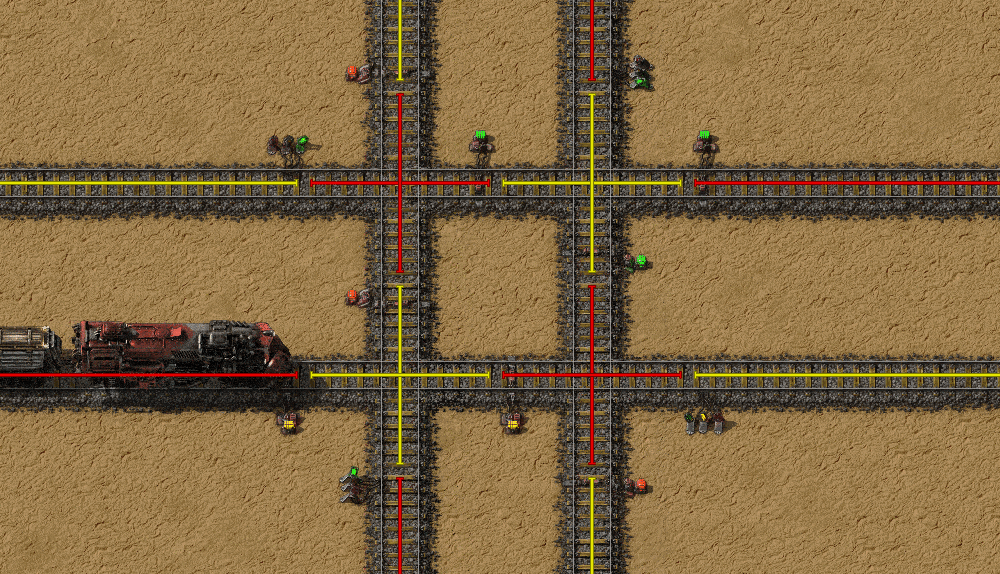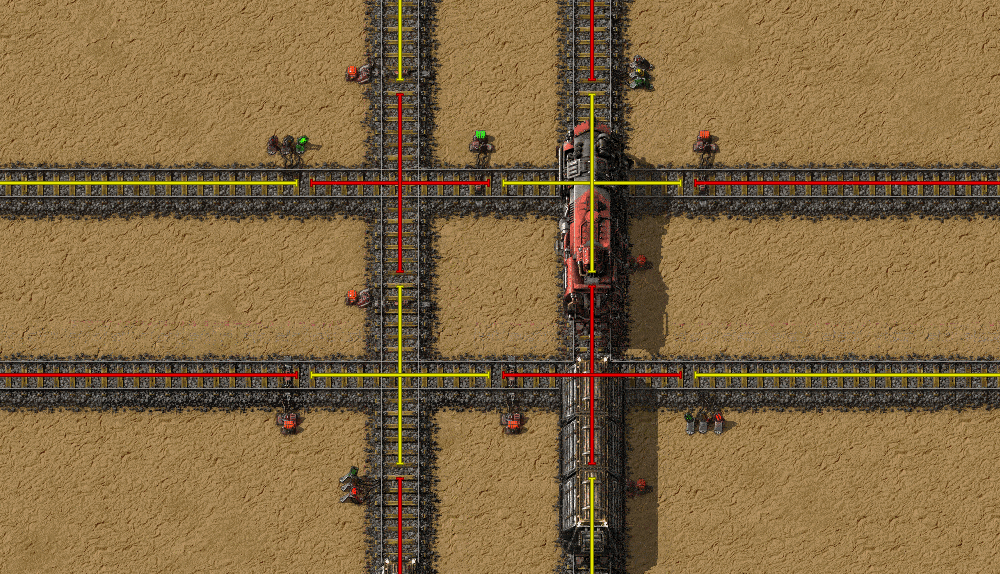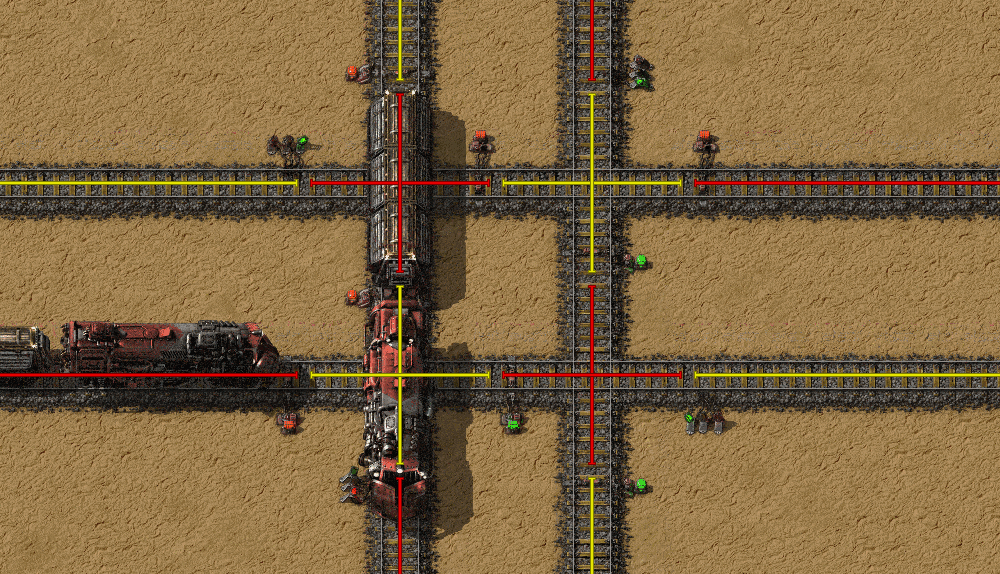
Double crossings are a common cause of train jams, as trains can stop in the middle of the crossing and block everything. It can even cause total deadlock, which require manual intervention to fix the problem. With chain signals, the rails that don't cross are still separated, but trains won't stop in the middle of the crossing.
Deadlock prevention
Another common cause of blockages are bidirectional single track lines with occasional bypasses. Here a train can't enter the line because another train is in it, but that train in turn can't leave the line.
With chain signals, this problem can be totally avoided by preventing the train from going to the shared section unless it can exit it.
Advanced
Some good pictures are at the Friday Facts #81 page.
- If the chain signal has only one exit, it doesn't allow the train to enter its block, if the exit block (which has a rail signal) is occupied.
- If in the block of the chain signal is a crossing, trains that cross the block can pass it, because a train waits before the chain signal, if the exit block isn't free.
- If there are more than one chain signal blocks before a regular block, a train waits before the first chain signal if the regular block isn't free.
- If a chain signal switches to green, all exits are free.
- If it switches to yellow, the block is reserved for a train and the signals of intersection blocks switch to red (like regular signal).
- If it switches to red, no exit is free.
- If it switches to blue, at least one exit is free.
History
- 0.16.0:
- Rail chain signals can be read by the circuit network.
- 0.12.0:
- Introduced