User:Hoeloe/sandbox
World generation is, in short, a number of settings which define what the world will look like once generated. This can dramatically alter gameplay- a new player is advised to start with the default settings before deciding to change their world.
Generation
How it works
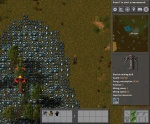
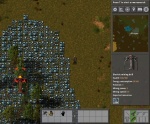
A more technical explanation of world generation mechanics is that the map generator generates most parts of the world with an algorithm named "Perlin Noise". In short, it works a bit like the waves in the sea.
Everything above a defined level defines the existing (or non-existing) features of some type of terrain. The player should also know that the map is not generated at game start. Only the parts they see are generated, everything else is not. The map will be generated gradually as the player explores more terrain. See below for more technical details.
The following image shows an example how the world generator might create a new map.
Algorithm
The map generator (world generator) is based on a modified Perlin noise algorithm. A more detailed description is in the API documentation.
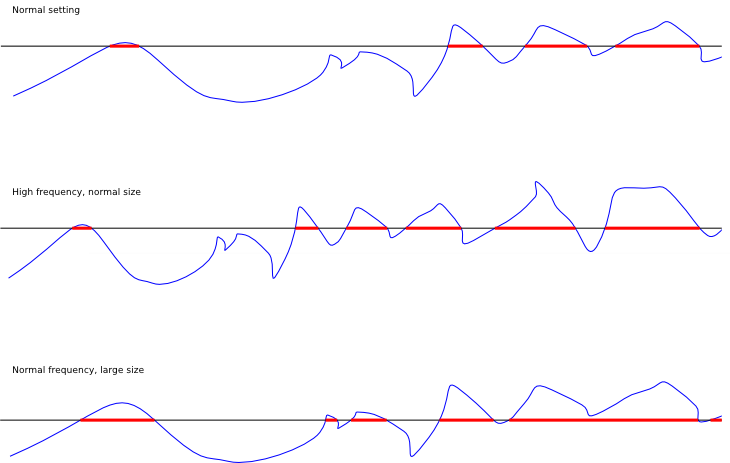
From the article which describes the generation:
Top: Normal settings, Middle: The same, but with higher frequency (note the same curve, but more condensed shape), Down: Same as top, but higher level = increased size.
The blue wavy line is an internal noise function, black line is a "level" that is used to determine resource placement, red lines are actual placed resources. The high frequency refers mainly to the noise function. Increasing the frequency increases count of resource fields and decreases their size and distance between them. This mechanism is used all through the map generation in factorio, with some adjustments. The map generator works tile by tile, so the resources are placed on a tile x if f(x) > 0. The amount of resources on the tile is given by f(x) * richness.
Generating new Chunks
A map is endless by default, though its size can be limited by height and width - see below. Because it is technically endless, the whole map isn't generated from the gamestart. A new Chunk of map is generated only when needed, similar to other procedurally generated world games.
Generating invisible Chunks
Outside of the visible chunk area, an invisible area of about 3 chunks wide is generated. This is used as a preloading mechanism and for biters outside of the visible chunks to be able to see the player (fog of war). Invisible chunks are also generated if pollution is generated heavily; the game generates (invisible) chunks as it needs to spread the pollution into the area.
Exploring
If the player arrives at the current visible borders the needed chunks are generated. As the player explores, a radius of about 3 chunks are continually loaded around them. As this can take a while on lower end machines, it is possible to outrun the world generator and end up in 'limbo' with no entities around the player. Staying still for a while will allow the generator to catch up.
Charting
As long as a chunk is invisible, the part of the players map stays black. This changes when a chunk is charted, which means when it is "touched" by radar. Either the players internal radar, which is always available and continually charts chunks around the player, or the Radar entity. When a visible chunk is generated there might be other chunks also invisibly generated.
An invisible chunk is eventually not made visible, even if you are so close, that you are able to see it in the character view (a black fog of war). This is, because of the above rule: a chunk is made visible, if it is touched by radar. Not character visibility. The players radar (or any radar) needs to be in range of that chunk to make it visible.
Maximum Map Size an user Memory
The map size is limited to 2000 x 2000 kilometers (a quadrant with 2,000,000 tiles side-length, an area of 4,000,000,000,000 quadrant-tiles). This is between the size of India and Australia. It would take around 240 game-minutes (=4 hours) by train to reach that border from the center. This means that the world is essentially endless.
Because only chunks are generated around the area that is revealed by radar, it is with current computers possible to reach that border. This is, because the needed memory size of the map is limited only by the generated number of chunks in the game. Which is not so much if you allocate just a small stripe of land.
The generated chunks are mapped and stored in the player's RAM, which is the limiting factor.
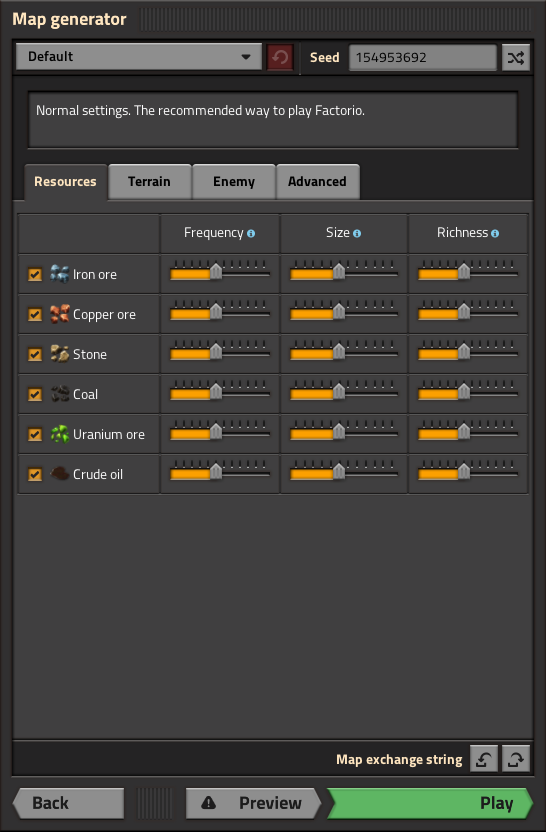
Configuration
Basic Settings
Presets
Peacefull Mode
The Enemies don't begin fights, only responding if the player attacks them. This can be also switched on during the game- look into Console commands.
Enable Replay
Map-width and -height
If the player limits the width and/or height they may generate maps with finite resources and area. This is recommended for multiplayer servers running on weaker machines or players seeking extra challenge. Another option is to make the world infinite in only one axis, this is commonly referred to as a ribbon world.
Map Seed
This is the starting value for the random number generator that Factorio uses for generating the world. Know that 'random number' is really a misnomer in Factorio and on computers in general, as they aren't really random, instead being calculated with complicated algorithms that require a seed as starting value (For more detail, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_seed).
So even with the same map-exchange string but a different seed maps can change dramatically, or appear very similar. It's up to chance. In order to get a true copy of a world, giving the map-exchange string and allowing the string to fill out the seed is important.
Map Exchange String
A string generally looks like so:
>>>AAALABAABgADAwYAAAAEAAAAY29hbAMDAgoAAABjb3BwZXItb3Jl AwMCCQAAAGNydWRlLW9pbAMDAgoAAABlbmVteS1iYXNlAwMCCAAAAGl yb24tb3JlAwMCBQAAAHN0b25lAwMCORcrDUQ7AACMCwAAAAAAAAAAAA ADAFR8w0Q=<<<
It is a string of good length that begins with >>> and ends with <<<. Many facilities exist within the community for sharing exchange strings. The map exchange string can be used in the map-generator: there is an extra field where the player can paste this string into. On windows computers, this may be done by selecting a string, right-clicking or pressing Control + C, then put it into the string field for the world generator with Control + V.
If you wish to retrieve the map-exchange string from your world:
In the Load Game dialog select the game whose string you want, then click the Map Exchange String button in the lower left corner. When the string pops up, highlight it with your mouse and press Control-C to copy it. (Command-C on Mac.) You can now paste it in the map generator to create a copy of that world, or send it to a friend.
For a technical description of the map exchange string, see Map Exchange String Format.
Resource Settings
Frequency
This is not, how frequent ore, coal, oil etc. is, instead determining the number of individual deposits the player will encounter.
This defines the wavelength of the wave-generators used by the Perlin Noise algorithm above, but not the total size of all the waves. This means that frequency doesn't modify the amount of resources on a tile, instead modifying the area of each deposit and the number of deposits. Additionally, changing frequency doesn't affect the average amount of resources in a limited map, only their distribution.
If resource frequency is increased, each of the deposits is smaller and has less resources in total (because it covers less area) and deposits are very common. If resource frequency is decreased, the deposits are larger but more rare. This also causes enemy bases to appear more often using the same distribution rules as ores - however, this can lead to rapid enemy expansion due to the much higher number of nest clusters.
Size
This defines the size of generated ore patches and water through defining "levels." It increases the average diameter of ore patches and lakes, allowing one to adjust the size of both of these.
It's as simple as it seems- Small size would mean small ore patches and water masses, large means large ore patches and water masses. Note that this is effected by frequency, though it is presumably able to increase the total ore and water of the world where frequency simply re-balances it.
Finally, this causes enemy bases to spawn larger, though bases created through the "natural process" of expansion are going to adhere to different rules.
The following table shows how the frequency and size settings affects the generation of ore patches. For more detail, open the images in a new tab.
| Frequency \ Size | Very small | Small | Medium | Big | Very big |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very low | 
|
|

|

|

|
| Low | 
|

|

|

|

|
| Normal | 
|

|

|

|

|
| High | 
|

|

|

|

|
| Very high | 
|

|

|

|

|
Richness
This defines the actual content of every ore patch and oil field. Resource field richness increases by distance.
| Very poor | Poor | Regular | Rich | Very rich |
|---|---|---|---|---|
The left column
- Water: How water is generated on each map.
- Copper, Stone, Coal, Crude oil: Resources required to progress in the game. See above for more detailed explanations about each of these changes.
- Enemy bases: How many and how large starting bases are. Note that new bases are created over time, making low enemy base counts somewhat less significant.
Advanced Settings
Pollution
Evolution
Enemy expansion
Recipes/Technology
Presets
Default
Rich Resources
Marathon
Dangerous
Death World
Train World
History
- 0.15.0:
- The world generator now has select-able presets.
- 0.13.0:
- Map generator algorithm changed, further resource field now have greater richness.