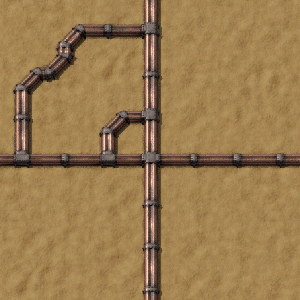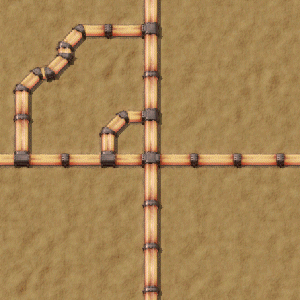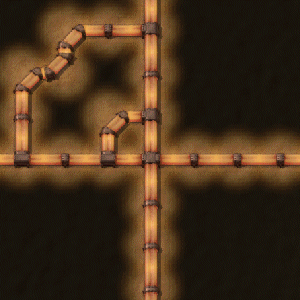
Heat pipe
| Heat pipe |
|
Recipe |
|
| + + → | |
|
Total raw |
|
| + + |
|
Map color |
|
|
Health |
200 |
|
Resistances |
Explosion: 0/30% |
|
Stack size |
50 |
|
Dimensions |
1×1 |
|
Maximum temperature |
1000 °C |
|
Mining time |
0.1 |
|
Prototype type |
|
|
Internal name |
heat-pipe |
|
Required technologies |
|
|
Produced by |
|
The heat pipe can transport heat over longer distances and connect devices which produce and use heat. Currently this is limited to heat exchangers and nuclear reactors.
Heat pipes have a heat capacity of 1 MJ/°C. Thus, they can theoretically buffer 500 MJ of heat energy across their working range of 500°C to 1000°C, making them a space-efficient energy store. However, because temperature needs a drop of greater than 1 degree before it will "flow," you can't raise them all the way to 1000°C or drain them all the way to 500°C, so the practical energy capacity will depend on the layout.
As heat pipes rise in temperature, they will give off a very low-distance glow.
History
- 0.17.67:
- Heat pipes (also in reactors and heat exchangers) glow with high temperatures.
- 0.15.11:
- Changed heat transfer mechanics, prior to this heat would flow better following the order of heat pipe placement
- 0.15.0:
- Introduced
See also