Arithmetic combinator: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(Undo orphaning of page) Tag: Undo |
||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Languages}} | {{Languages}} | ||
{{ | {{:Infobox:Arithmetic combinator}} | ||
The arithmetic combinator is part of the [[circuit network]] and one of three types of combinators available in the game (along with the [[constant combinator]] and [[decider combinator]]). Each arithmetic combinator can perform any one of the following mathematical operations on signals, and will show the corresponding symbol on its top: | |||
[[File: | [[File:arith_combinator_anim.png]] | ||
* addition (<span style="color:yellow">+</span>) | |||
* subtraction (<span style="color:yellow">−</span>) | |||
* multiplication (<span style="color:yellow">*</span>) | |||
* division (<span style="color:yellow">/</span>) | |||
* modulo (<span style="color:yellow">%</span>) | |||
* exponentiation (<span style="color:yellow">^</span>) | |||
* left bit shift (<span style="color:cyan"><<</span>) | |||
* right bit shift (<span style="color:cyan">>></span>) | |||
* bitwise AND (<span style="color:cyan">&</span>) | |||
* bitwise OR (<span style="color:cyan">|</span>) | |||
* bitwise XOR (<span style="color:cyan">^</span>) | |||
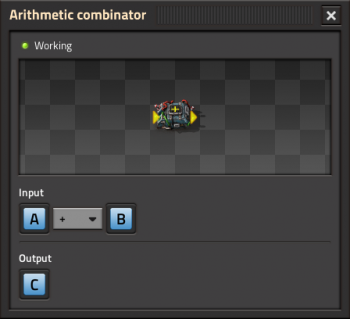
==Function== | The arithmetic combinator accepts two input connections (red and green wires), and sends its output to both output connections. The input wires connect to the nubs on the left side of the sprite in the sidebar, while the outputs connect to the right side. | ||
[[File:Arithmetic_combinator_gui.png|350px|GUI of the Arithmetic Combinator.]]<br /> | |||
== Function == | |||
The internal logic process has three steps: | The internal logic process has three steps: | ||
# All input signals on the red and green wires are summed within the combinator. | |||
# The specified operation is performed on the selected signal(s). | |||
# The result of this operation is output as the selected output signal. | |||
The left operand of the operation can be any single signal or the [[Virtual signals#Each|''each'' virtual signal]], and the right operand can be any single signal or a constant value. | |||
If the left operand is a single signal, the output must be a single signal. The operation is performed on the values of the chosen left and right signals, and the result is sent to the output on the specified signal. | |||
If the left operand is the ''each'' signal, then the output can be a single signal or the ''each'' signal. If the output is the ''each'' signal, then the operation is performed individually on the value of each input signal along with the value of the right operand, and each result is sent to the output on the same signal. If the output is a single signal, the operation is done on each of the input signals, the individual results are all added together, and that result is sent to the output on the specified signal. | |||
The | == Notes on operations == | ||
When using '''division''', the result is truncated: | |||
* 21 / 10 = 2 | |||
* 19 / 10 = 1 | |||
* −21 / 10 = −2 | |||
* −19 / 10 = −1 | |||
* 21 / −10 = −2 | |||
* 19 / −10 = −1 | |||
* −21 / −10 = 2 | |||
* −19 / −10 = 1 | |||
'''Modulo''', indicated using % as it is in most programming languages, is the remainder after division. For example, 13 % 3 is 1 (13 = 4 * 3 + 1). This can, for example, be combined with truncated division as described above to separate out individual digits of a number for use in building visual indicators: | |||
* (24321 / 10000) % 10 = 2 | |||
* (24321 / 1000) % 10 = 4 | |||
* (24321 / 100) % 10 = 3 | |||
* (24321 / 10) % 10 = 2 | |||
* (24321 / 1) % 10 = 1 | |||
Negating the left operand of a modulo negates the result, while negating the right operand does nothing: | |||
* 13 % 3 = 1 | |||
* 13 % −3 = 1 | |||
* −13 % 3 = −1 | |||
* −13 % −3 = −1 | |||
'''Left bit shift''' and '''Right bit shift''' are not arithmetic. Instead these options deals with numbers in the [[:Wikipedia:Binary_number|binary]] state. The 0's and 1's that make up a number are shifted in the specified direction which can result in a completely different number, due to the change in the binary value. | |||
[[File:Bitshiftleft.png|none|thumb|200px|Example of a 'left bit shift'.]] | |||
== History == | |||
{{history|0.15.0| | |||
* Added Modulo, Power, Left Bit Shift, Right Bit Shift, Bitwise AND, Bitwise OR and Bitwise XOR to the Arithmetic Combinator.}} | |||
{{history|0.13.0| | |||
* Connected wires are highlighted when hovering over a combinator connected to the [[circuit network]]. | |||
* Combinators show input and output in alt mode. | |||
* More virtual signals for combinators. | |||
* Constant combinator can be rotated. | |||
* Decider combinator "input count" option makes the combinator copy the count of the specified output signal from the input signals, instead of copying the count from the condition. | |||
* New combinator graphics. }} | |||
{{history|0.12.5| | |||
* Combinators now emit light.}} | |||
{{history|0.12.2| | |||
* Combinators no longer turn off when no wires are connected.}} | |||
{{history|0.12.0| | |||
* Introduced}} | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Decider | *[[Decider combinator]] | ||
*[[Constant | *[[Constant combinator]] | ||
*[[Combinator | *[[Tutorial:Combinator tutorial|Combinator tutorial]] | ||
*[[Circuit network]] | *[[Circuit network]] | ||
*[[Tutorial:Circuit network cookbook|Circuit network cookbook]] | |||
{{LogisticsNav}} | |||
{{C|Circuit network}} | |||
Latest revision as of 17:18, 17 December 2021
| Arithmetic combinator |
|
Recipe |
|
| + + → | |
|
Total raw |
|
| + + |
|
Recipe |
|
| + + → | |
|
Total raw |
|
| + + |
|
Map color |
|
|
Health |
150 |
|
Stack size |
50 |
|
Energy consumption |
1 kw (electric) |
|
Mining time |
0.1 |
|
Prototype type |
|
|
Internal name |
arithmetic-combinator |
|
Required technologies |
|
|
Produced by |
|
The arithmetic combinator is part of the circuit network and one of three types of combinators available in the game (along with the constant combinator and decider combinator). Each arithmetic combinator can perform any one of the following mathematical operations on signals, and will show the corresponding symbol on its top:
- addition (+)
- subtraction (−)
- multiplication (*)
- division (/)
- modulo (%)
- exponentiation (^)
- left bit shift (<<)
- right bit shift (>>)
- bitwise AND (&)
- bitwise OR (|)
- bitwise XOR (^)
The arithmetic combinator accepts two input connections (red and green wires), and sends its output to both output connections. The input wires connect to the nubs on the left side of the sprite in the sidebar, while the outputs connect to the right side.
Function
The internal logic process has three steps:
- All input signals on the red and green wires are summed within the combinator.
- The specified operation is performed on the selected signal(s).
- The result of this operation is output as the selected output signal.
The left operand of the operation can be any single signal or the each virtual signal, and the right operand can be any single signal or a constant value.
If the left operand is a single signal, the output must be a single signal. The operation is performed on the values of the chosen left and right signals, and the result is sent to the output on the specified signal.
If the left operand is the each signal, then the output can be a single signal or the each signal. If the output is the each signal, then the operation is performed individually on the value of each input signal along with the value of the right operand, and each result is sent to the output on the same signal. If the output is a single signal, the operation is done on each of the input signals, the individual results are all added together, and that result is sent to the output on the specified signal.
Notes on operations
When using division, the result is truncated:
- 21 / 10 = 2
- 19 / 10 = 1
- −21 / 10 = −2
- −19 / 10 = −1
- 21 / −10 = −2
- 19 / −10 = −1
- −21 / −10 = 2
- −19 / −10 = 1
Modulo, indicated using % as it is in most programming languages, is the remainder after division. For example, 13 % 3 is 1 (13 = 4 * 3 + 1). This can, for example, be combined with truncated division as described above to separate out individual digits of a number for use in building visual indicators:
- (24321 / 10000) % 10 = 2
- (24321 / 1000) % 10 = 4
- (24321 / 100) % 10 = 3
- (24321 / 10) % 10 = 2
- (24321 / 1) % 10 = 1
Negating the left operand of a modulo negates the result, while negating the right operand does nothing:
- 13 % 3 = 1
- 13 % −3 = 1
- −13 % 3 = −1
- −13 % −3 = −1
Left bit shift and Right bit shift are not arithmetic. Instead these options deals with numbers in the binary state. The 0's and 1's that make up a number are shifted in the specified direction which can result in a completely different number, due to the change in the binary value.
History
- 0.15.0:
- Added Modulo, Power, Left Bit Shift, Right Bit Shift, Bitwise AND, Bitwise OR and Bitwise XOR to the Arithmetic Combinator.
- 0.13.0:
- Connected wires are highlighted when hovering over a combinator connected to the circuit network.
- Combinators show input and output in alt mode.
- More virtual signals for combinators.
- Constant combinator can be rotated.
- Decider combinator "input count" option makes the combinator copy the count of the specified output signal from the input signals, instead of copying the count from the condition.
- New combinator graphics.
- 0.12.5:
- Combinators now emit light.
- 0.12.2:
- Combinators no longer turn off when no wires are connected.
- 0.12.0:
- Introduced